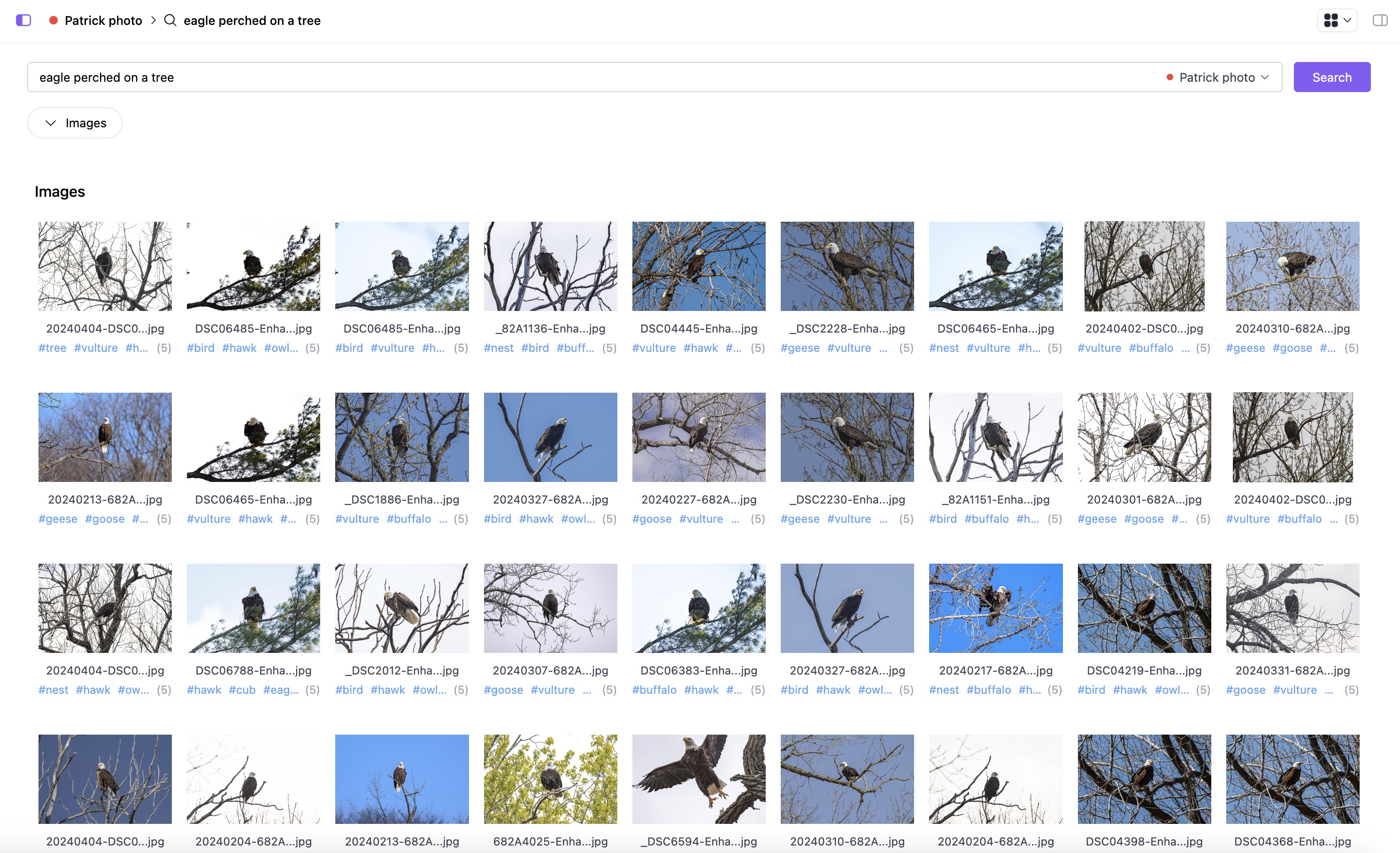
Indexing Assets with Shade
Indexing is a core feature of Shade. This allows you to specifically AI index certain files for better search results of those assets.
💡 Note: Whenever you add assets to a drive, we automatically do full text search and metadata extraction, but do not automatically do AI indexing, you must explicitly AI index certain folders, that way you get to choose what you would like to search and keep your search index clean
Shade is built from the ground up with proprietary AI that understands your files and assets for what they are, not what they’re named. But we only do this on the assets that you want us to index. As a result, if you want to leverage Shade’s global search capabilities or upgraded neural file search, then you want to index your assets.
Indexing Files and Folders
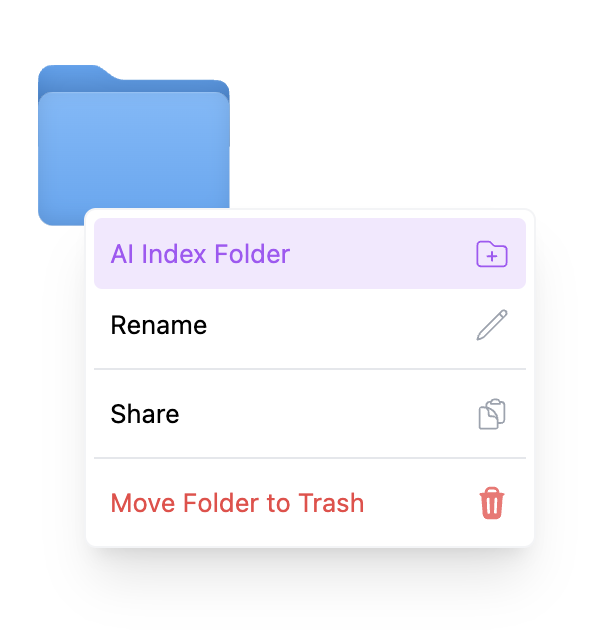
To get started - simply head to the file or folder that is in your drive, right click, and hit “index with Shade”. Shade will then parse through this directory with its AI in order to properly index the assets that are found within the file and folder.
For the full list of files that Shade supports, please check here (opens in a new tab).
Once a folder or an individual file is directly added to Shade via right click, it is considered an Indexed Root by Shade.
Removing Indexed Roots
If you decide that you wish to remove a folder from the search index, you can do this by heading into settings, files and folders, and selecting the file(s) and folder(s) that you wish to remove from the index. These will remove all AI metadata about the file. Any user metadata, and file metadata, however, will be kept (except for in Catalog Drives where all data will be removed)
💡 Note: Only drive managers have the ability to add or remove indexed roots
Search and Drive Permissions
Users will be able to search only for the files and folders that the user has access to. If a Guest is added to a folder, they will only be able to search the contents of that folder. If a Guest is added at the drive level, they will be able to search all assets at the drive level.